Authentication¶
This documentation explains the main mechanism of authentication.
Overview¶
Main host mechanisms are located in apps.auth.
Login is internally based on a token authentication: each user session is associated to a token.
There is a common access point, auth which can be used to log out, but to log in, each authentication mechanism use its own endpoint (auth_db and auth_xmpp so far). This way each endpoint can use its own schema validation while the common endpoint can be called for logout, allowing several auth mechanisms to be running at the same time.
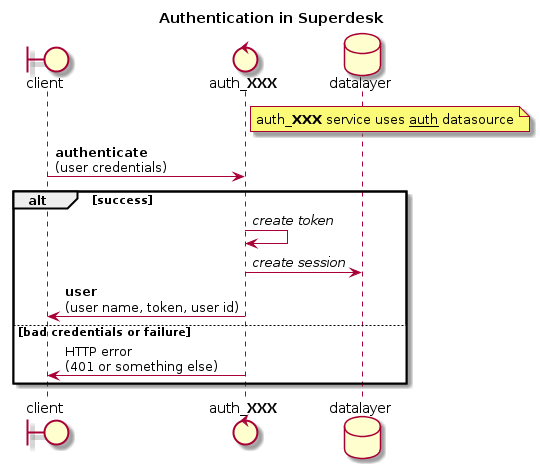
Adding a new authentication mechanism¶
Adding a new authentication mechanism is done by creating a new endpoint extending the basic service. The new endpoint should be named auth_XXX where XXX is a short name for the new mechanism.
The auth module provide the base features, with main service.
-
class
apps.auth.service.AuthService(datasource=None, backend=None)¶ -
authenticate(document)¶ Authenticate user according to credentials
Parameters: documents – credentials for this authentication mechanism Returns: authenticated user Raise: CredentialsAuthError if authentication is invalid
-
on_deleted(doc)¶ Runs on delete of a session
Parameters: doc – A deleted auth doc AKA a session Returns:
-
update_session(updates=None)¶ Update current session with given data.
Parameters: updates – updates to be made
-
To implement its authentication mechanism, a module need to override the authenticate method.
When creating a service based on AuthService, the authentication module must use the auth datasource instead of its own endpoint name. This allow several auth methods to use the same session system and to logout from auth common endpoint.
Special case: auth_db¶
auth_db is used for the basic database login/password authentication. In some cases it may be desirable to replace this mechanism (e.g. this is the case with LDAP). This is done by using the same endpoint name, and avoiding the import of apps.auth.db module. The login/pass default login interface in the client will then stay unchanged.
Other uses of apps.auth¶
Following functions can be used:
-
apps.auth.get_user(required=False)¶ Get user authenticated for current request.
Parameters: required (boolean) – if True and there is no user it will raise an error
-
apps.auth.get_user_id(required=False)¶ Get authenticated user id.
Parameters: required (boolean) – if True and there is no user it will raise an error
-
apps.auth.is_current_user_admin(required=False)¶ Test if current user is administrator.
Parameters: required – raise an error if required and there is no user context
Superdesk OAuth¶
Superdesk OAuth support
New in version 1.9.
There is oauth resource for authenticating users by email.
Email must be provided by trusted identity service, eg. Google.
The authentication flow with js client is:
- Client opens server api url in a new window,.
- There is a redirect to auth provider (eg. Google).
- Once authenticated user is redirected back to server api url.
- There user email from auth provider is used to authenticate user.
- Template is rendered with session data which sends message to parent window and popup is closed.
-
superdesk.auth.auth_user(email)¶ Authenticate user via email.
This will create new session for user and render template with session data which is used by client to setup authentication.
Parameters: email – user email address
Superdesk Google OAuth¶
Superdesk Google Authentication
New in version 1.8.
You can use Google for authentication, first you have to create credentials in Google API console:
set your client URL as Authorized JavaScript origins:
https://example.com
set server URL +
/api/login/google_authorizedas Authorized redirect URIs:https://example.com/api/login/google_authorized
Once configured you will find there Client ID and Client secret, use both to populate Google OAuth Settings.
Changed in version 1.9: There is no need to configure client, it reads config from server now.
Changed in version 1.9: Login url is /api/login/google_authorized instead of /login/google_authorized.